Thyroid Cancer
What is thyroid cancer?
Thyroid cancer is the most common endocrine system cancer. Thyroid cancer occurs when thyroid nodules become cancerous. Thyroid nodules that are cancerous need to be removed to protect thyroid function and prevent thyroid cancer from spreading in the body. The estimated incidence rate of thyroid cancer in various parts of the world ranges from 0.5 to 10 cases per 100,000 persons per year. It is the fastest-growing cancer in the United States in both men and women, with over 62,000 new cases diagnosed every year.
Surgery
If the FNA of the thyroid nodule confirms cancer, she will refer you to an experienced endocrine surgeon for thyroid surgery. Surgery is used to remove all the tumor and all or part of the thyroid gland and any abnormal lymph nodes in the neck. Following surgery, she will review the pathology findings with you and coordinate further management if needed.
Thyroid hormone replacement therapy
If your thyroid gland is partially or completely removed, you must take daily thyroid hormone replacement pills. Thyroid hormone therapy is also used to lower blood TSH levels to help prevent thyroid cancer recurrence.
Radio iodine therapy
Following surgery, if you require radioiodine therapy, Dr. Thomas will refer you for radioiodine therapy to a nuclear medicine specialist.
Immunotherapy
In advanced or aggressive thyroid cancer, you will be referred to an oncologist for further management.
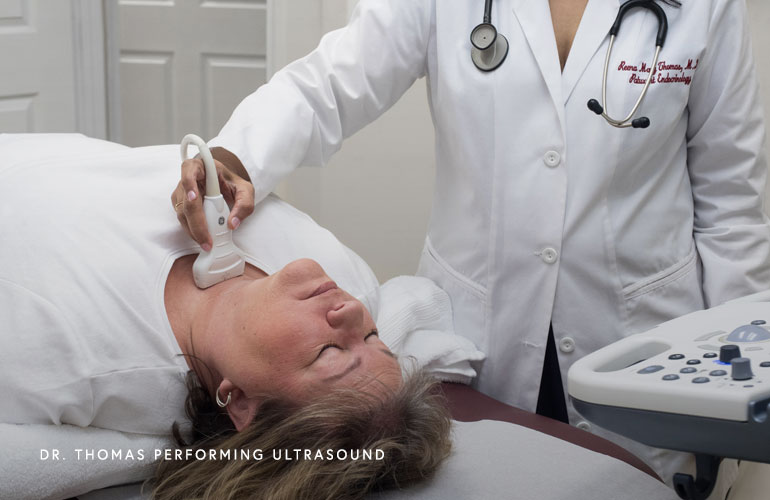
Lifelong surveillance for the recurrence of thyroid cancer is mandatory. Dr Thomas will see you at regular intervals and do a comprehensive evaluation, including physical examinations and appropriate blood tests to monitor your thyroid hormone replacement therapy and tumor markers. She will also do an ultrasound of the neck at regular intervals to monitor for any recurrence of thyroid cancer.
At a Glance
Dr. Reena Thomas, MD
- Dual American board-certified endocrinologist
- Author of numerous academic and clinic research
- Learn more
